状态管理
在实际的 React 项目中会存在多个组件,每个组件的 state 是由自身进行管理,包括组件定义自身的 state、组件之间的通信通过 props 传递、或者使用 Context 实现数据共享。
如果让每个组件都存储自身相关的状态,理论上来讲不会影响应用的运行,但在开发及后续维护阶段,将花费大量精力去查询状态的变化过程。
这种情况下,如果将所有的状态进行集中管理,当需要更新状态的时候,仅需要对这个管理集中处理,而不用去关心状态是如何分发到每一个组件内部的。
第一章:Redux
一、是什么
A Predictable State Container for JS Apps 是 Redux 官方对于 Redux 的描述,这句话可以翻译为“一个专为 JS 应用设计的可预期的状态容器”。
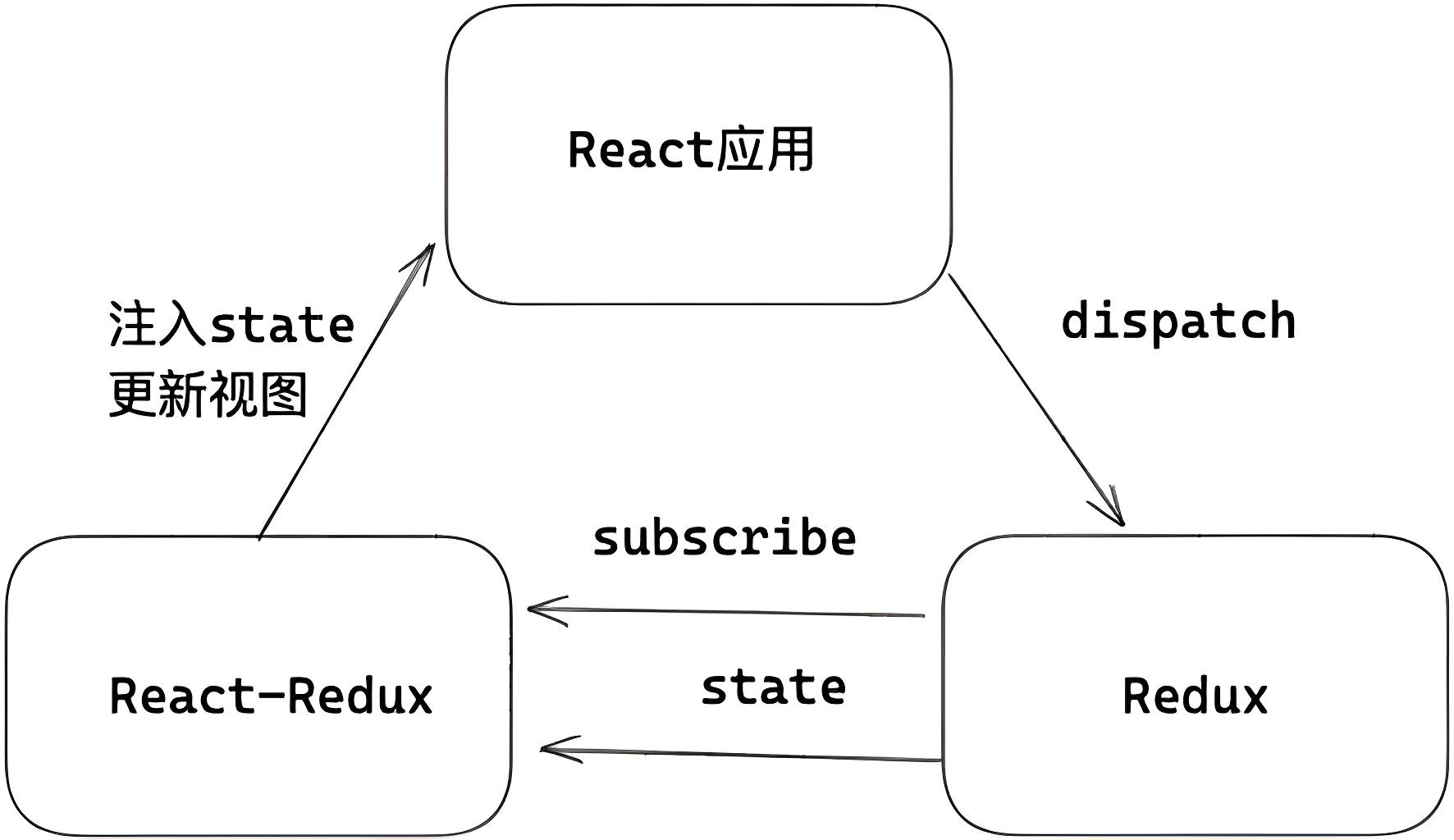
React-Redux、Redux、React 三者什么关系?
Redux:一个应用状态管理 js 库,可以应用于其他框架构建的前端应用,与 React 没有半毛钱关系。
React-Redux:连接 React 应用和 Redux 状态管理的桥梁。主要专注两件事,一是如何向 React 应用中注入 redux 中的 Store;二是如何根据 Store 的改变,把消息派发给应用中需要状态的每一个组件。
redux 就是一个实现上述集中管理的容器,遵循三大基本原则:
- 单向数据流。
- state 是只读的。
- 使用纯函数来执行修改。
二、工作原理
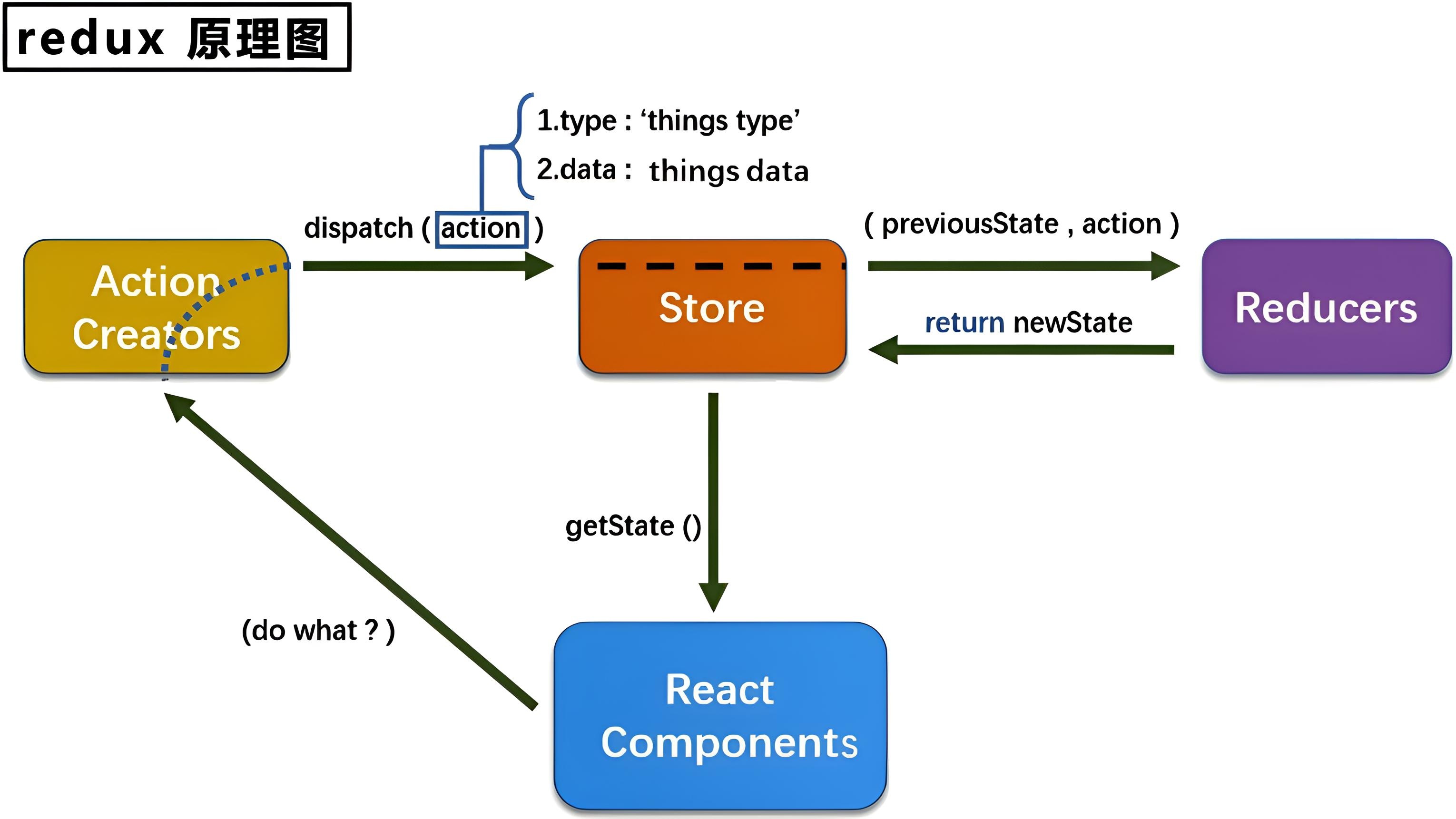
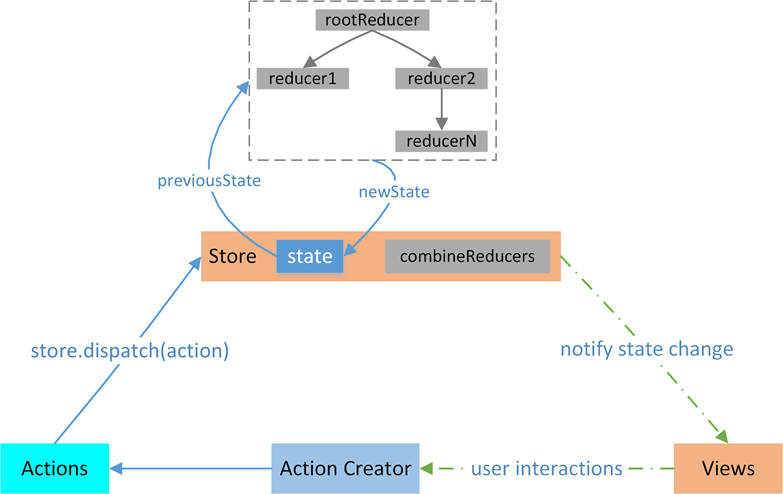
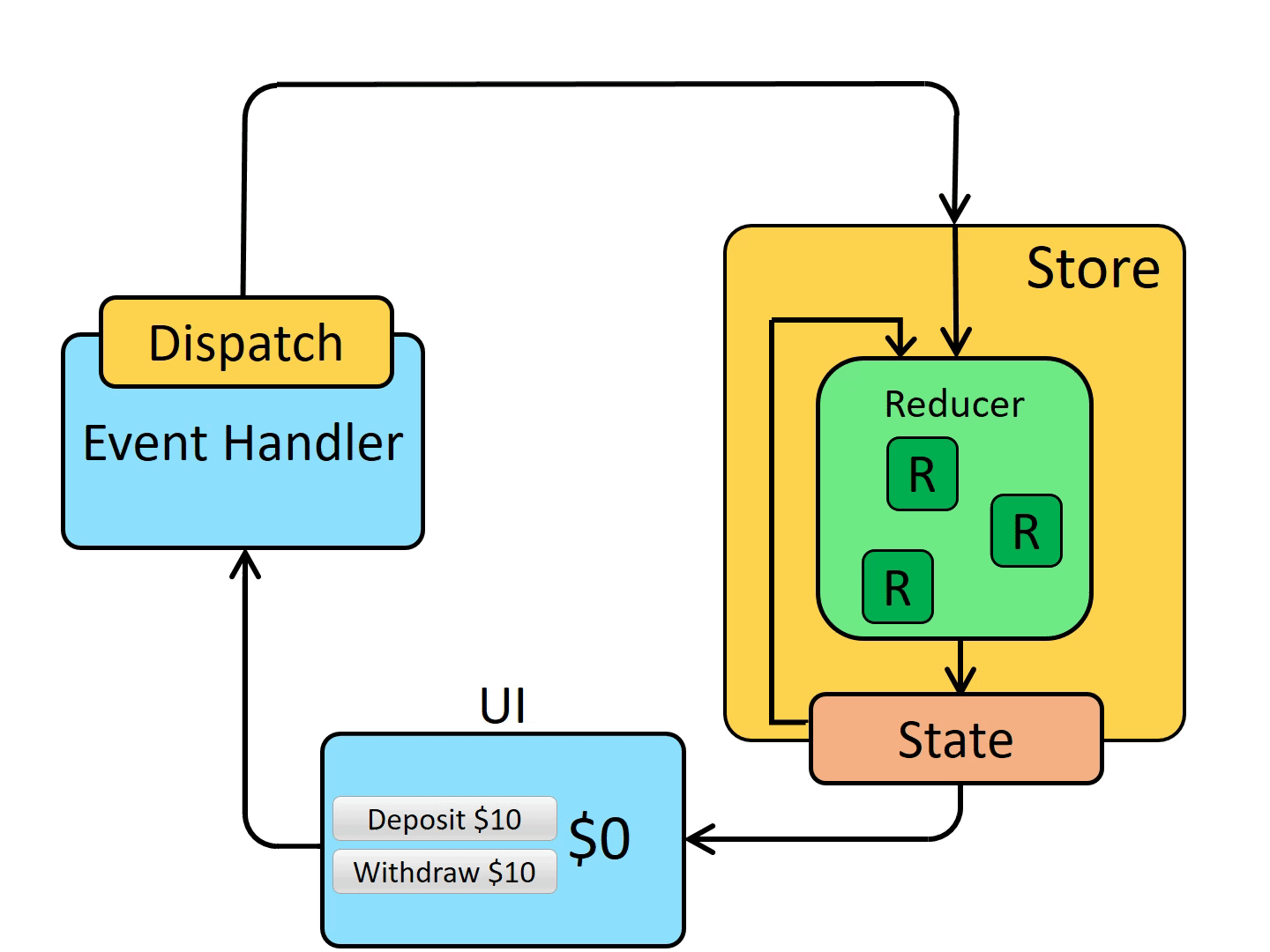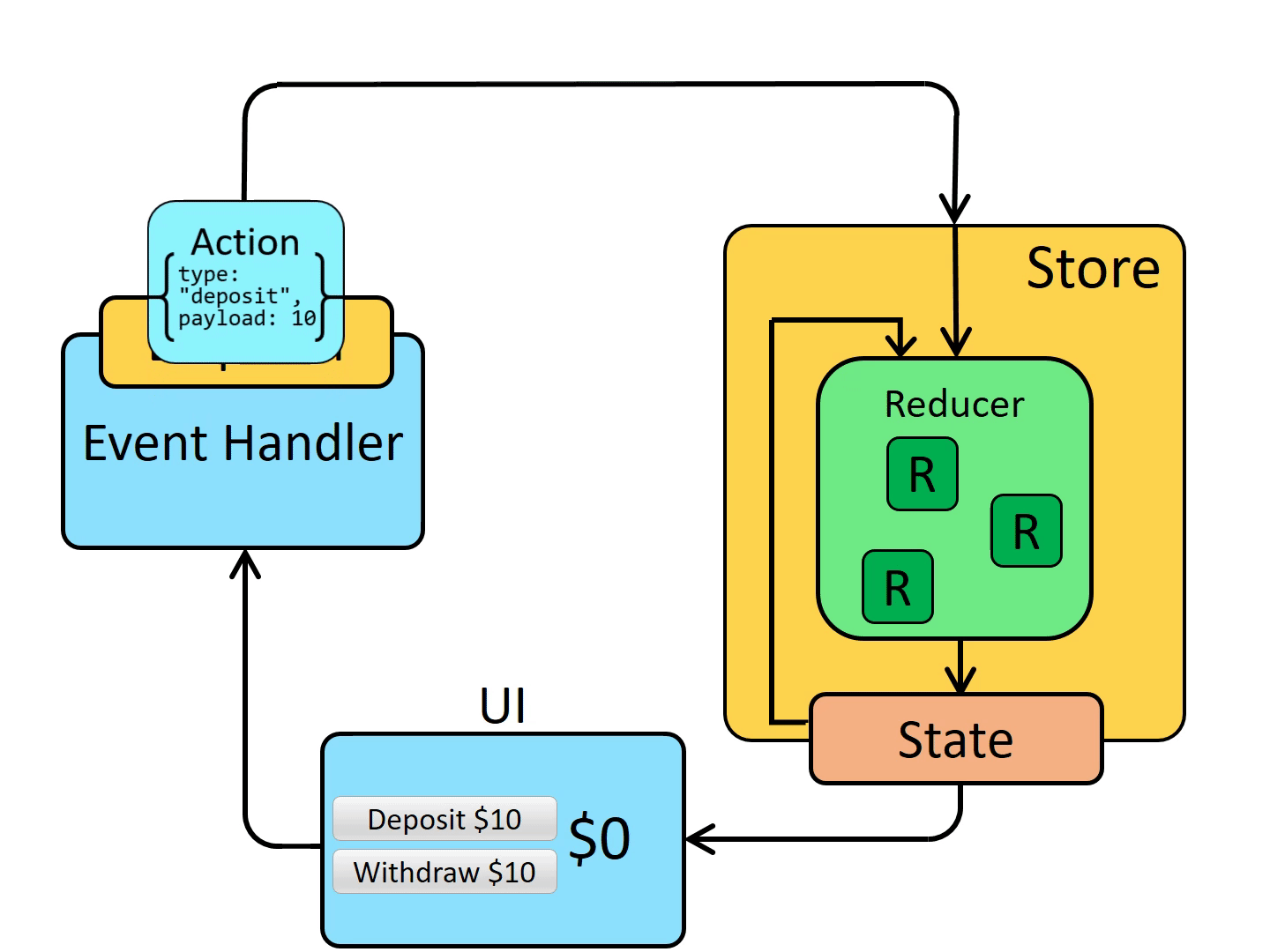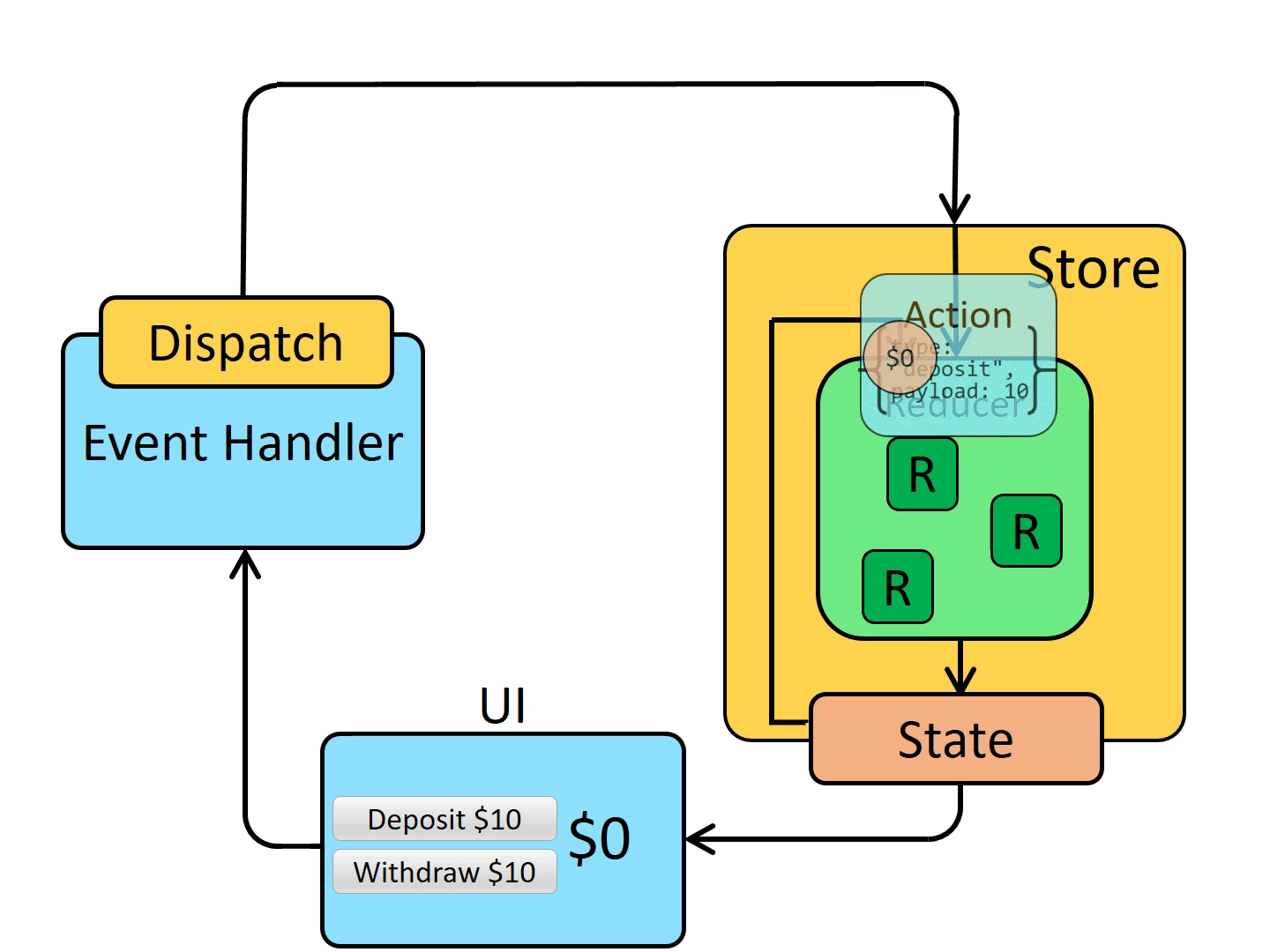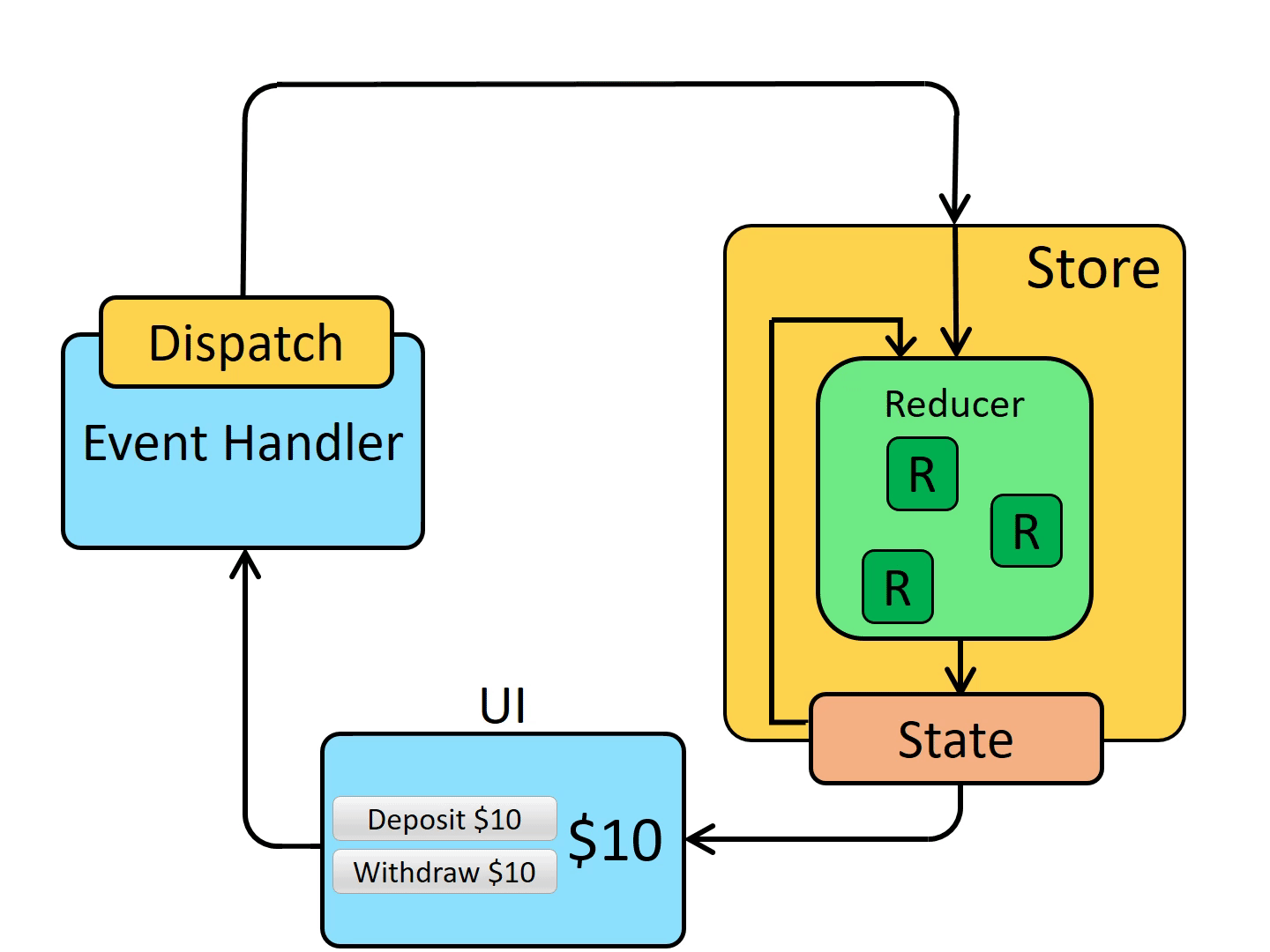
首先组件会在 Redux 中派发一个 action 方法,通过调用 store.dispatch 方法,将 action 对象派发给 store,当 store 接收到 action 对象时,会将先前的 state 与传来的 action 一同发送给 reducer,reducer 在接收到数据后,进行数据的更改,返回一个新的状态给 store。最后,当 store 监听到 state 的变化,就会调用监听函数,触发视图的重新渲染。
三、核心概念
1. store
store 是 Redux 的核心,可以理解为是 Redux 的数据中台。可以将任何我们想要存放的数据放在 store 中,在我们需要使用这些数据时,可以从中取出相应的数据。
1)API 用法介绍
因此需要先创建一个 store,在 Redux 中可以使用 createStore API 来创建一个 store。
const Store = createStore(rootReducer,initialState,middleware)
/*
const Store = createStore(rootReducer,initialState,middleware)
参数一 reducers :redux 的 reducer ,如果有多个那么可以调用 combineReducers 合并。
参数二 initialState :初始化的 state 。(可选参数)
参数三 middleware :如果有中间件,那么存放 redux 中间件。(可选参数)
*/正常状态可以会有多个 reducer,使用 combineReducers 可以合并多个 reducer。
/* 将 number 和 PersonalInfo 两个 reducer 合并 */
const rootReducer = combineReducers({ number:numberReducer,info:infoReducer })applyMiddleware 用于注册中间件。支持多个参数,每一个参数都是一个中间件。每次触发 action,中间件会依次执行。
const middleware = applyMiddleware(logMiddleware)在 store 对象下有一些常用的内置方法。
获取当前时刻的 store,采用 getStore 方法。
const state = store.getState();在前面我们的流程图中,通过 store 中的 dispatch 方法来派生一个 action 对象给 store。
store.dispatch(`action对象`)最后还有一个 subscribe 方法,这个方法可以帮助我们订阅 store 的改变,只要 store 发生改变,这个方法的回调就会执行。
为了监听数据的更新,我们可以将 subscribe 方法绑定在组件挂载完毕生命周期函数上,但是这样,当我们的组件数量很多时,会比较的麻烦,因此我们可以直接将 subscribe 函数用来监听整个 App 组件的变化。
store.subscribe(() => {
ReactDOM.render( <App /> , document.getElementById('root'))
})2)使用
在生产中,需要在 src 目录下的 redux 文件夹中新增一个 store.js 文件,在这个文件中,创建一个 store 对象,并暴露它。
第一步:从 redux 中暴露方法。
import {
createStore,
combineReducers,
applyMiddleware,
} from 'redux'并引入为 count 组件服务的 reducer。
import countReducer from './count_reducer'最后调用 createStore 方法来暴露 store。
export default createStore(countReducer, applyMiddleware(thunk))2. action
1)API 用法介绍
state 的变化,会导致视图的变化。但是,用户接触不到 state,只能接触到视图。所以,state 的变化必须是由视图发起的。
action 就是视图发出的通知,通知 store,此时的 state 应该要发生变化了。
action 是一个对象。其中的 type 属性是必须的,表示 action 的名称。其他属性可以自由设置,社区有一个规范可以参考:
const action = {
type: 'ADD_TODO',
payload: 'Learn Redux' // 可选属性。或者 data 属性代替 payload 属性
};Action Creator
view 要发送多少种消息,就会有多少种 action,如果都手写,会很麻烦。可以定义一个函数来生成 action,这个函数就称作 Action Creator。如下面代码中的 addTodo 函数:
const ADD_TODO = '添加 TODO';
function addTodo(payload) {
return {
type: ADD_TODO,
payload
}
}
const action = addTodo('Learn Redux');redux-actions 是一个实用的库,让编写 redux 状态管理变得简单起来。该库提供了 createAction 方法用于创建动作创建器:
import { createAction } from "redux-actions"
export const INCREMENT = 'INCREMENT'
export const increment = createAction(INCREMENT)上边代码定义一个动作 INCREMENT,然后通过 createAction,创建了对应 Action Creator:
- 调用 increment() 时就会返回
{ type: 'INCREMENT' } - 调用 increment(10) 返回
{ type: 'INCREMENT', payload: 10 }
2)使用
[1] 实现同步
action 是 store 中唯一的数据来源。一般来说,会通过调用 store.dispatch 将 action 传到 store。
import { createStore } from 'redux';
import { createAction } from "redux-actions";
const store = createStore(reducer, [preloadedState], [enhancer]);
const ADD_TODO = 'ADD_TODO';
const add_todo = createAction(ADD_TODO); // 创建 Action Creator
store.dispatch(add_todo('Learn Redux'));[2] 实现异步
一开始,直接调用一个异步函数,这虽然没有什么问题,但是难道 redux 就不可以实现了吗?
incrementAsync = () => {
const { value } = this.selectNumber;
const { count } = this.state;
setTimeout(() => {
this.setState({ count: count + value * 1 });
}, 500);
}可以先尝试将它封装到 action 对象中调用。
export const createIncrementAsyncAction = (data, time) => {
// 无需引入 store ,在调用的时候是由 store 调用的
return (dispatch, getState) => {
setTimeout(() => {
dispatch(createIncrementAction(data))
}, time)
}
}当我们点击异步加操作时,我们会调用这个函数,在这个函数里接收一个延迟多长时间,还有 action 所需的数据,和原先的区别只在于返回的是一个定时器函数。
但是如果仅仅这样,很显然是会报错的,它默认需要接收一个对象。

如果我们需要实现传入函数,那我们就需要告诉:你只需要默默的帮我执行以下这个函数就好!
这时我们就需要引入中间件,在原生的 redux 中暴露出 applyMiddleware 中间件执行函数,并引入 redux-thunk 中间件(需要手动下载)。
import thunk from 'redux-thunk'通过第二个参数传递下去就可以了。
export default createStore(countReducer, applyMiddleware(thunk))注意:异步 action 不是必须要写的,完全可以自己等待异步任务的结果后再去分发同步 action。
3. reducer
store 收到 action 以后,必须给出一个新的 state,这样视图才会进行更新。state 的计算(更新)过程则是通过 reducer 实现。
reducer 是一个函数,它接受 action 和当前 state 作为参数,返回一个新的 state:
const reducer = function (state, action) {
// ...
return new_state;
};为了实现调用 store.dispatch 方法时自动执行 reducer 函数,需要在创建 store 时,将 reducer 传入 createStore 方法:
import { createStore } from 'redux';
const reducer = function (state, action) {
// ...
return new_state;
};
const store = createStore(reducer);上面代码中,createStore 方法接受 reducer 作为参数,生成一个新的 store。以后每当视图使用 store.dispatch 发送给 store 一个新的 action,就会自动调用 reducer 函数,得到更新的 state。
举例:对接收的 action 中传来的 type 进行判断。
const initState = 0;
export default function countReducer(preState = initState, action) {
const {type, payload} = action;
switch (type) {
case INCREMENT:
return preState + payload
case DECREMENT:
return preState - payload
default:
return preState
}
}更改数据,返回新的状态。
上面写法有点麻烦,可以使用 redux-actions 简化。使用 handleActions 方法用于处理多个 action,不需要写 switch-case 语句。
// 使用方法:
// handleActions(reducerMap, defaultState)
import { handleActions } from 'redux-actions';
const initialState = {
counter: 0
};
const reducer = handleActions(
{
INCREMENT: (state, action) => ({
counter: state.counter + action.payload
}),
DECREMENT: (state, action) => ({
counter: state.counter - action.payload
})
},
initialState
);四、原生使用
点我查看代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Redux Counter</title>
<!-- 引入 Redux 和 Redux-actions -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/redux@latest/dist/redux.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/redux-actions@latest/dist/redux-actions.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Redux Counter</h1>
<p>Count: <span id="count">0</span></p>
<button id="increment">+1</button>
<button id="decrement">-1</button>
<script>
// 1. 创建 action creators
const increment = ReduxActions.createAction('INCREMENT');
const decrement = ReduxActions.createAction('DECREMENT');
// 2. 初始状态
const initialState = {
count: 0
};
// 3. 创建 reducer
const reducer = ReduxActions.handleActions({
INCREMENT: (state, action) => ({
count: state.count + 1
}),
DECREMENT: (state, action) => ({
count: state.count - 1
})
}, initialState);
// 4. 创建 store
const store = Redux.createStore(reducer);
// 5. 订阅更新
store.subscribe(() => {
document.getElementById('count').textContent = store.getState().count;
});
// 6. 添加事件监听
document.getElementById('increment').addEventListener('click', () => {
store.dispatch(increment());
});
document.getElementById('decrement').addEventListener('click', () => {
store.dispatch(decrement());
});
</script>
</body>
</html>第二章:React-Redux
一、类式组件操作
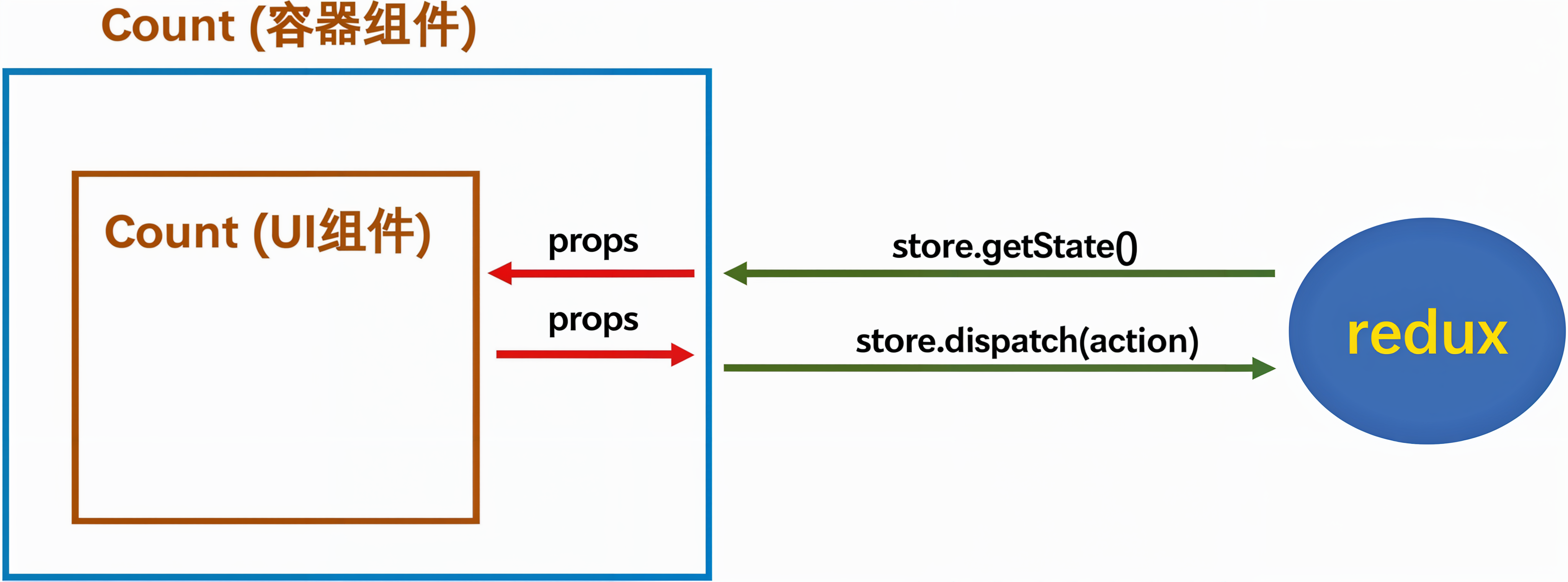
1. 模型图
1)所有的 UI 组件都需要有一个容器组件包裹。
2)容器组件来负责和 Redux 打交道,可以随意使用 Redux 的 API。UI 组件无任何 Redux API。
3)容器组件用于处理逻辑,UI 组件只会负责渲染和交互,不处理逻辑。
2. 基本使用
1)连接
连接 UI 组件
首先,在 src 目录下,创建一个 containers 文件夹,用于存放各种容器组件,在该文件夹内创建 Count 文件夹,即表示即将创建 Count 容器组件,再创建 index.jsx 编写代码。
小贴士:在生产当中,可以直接将 UI 组件写在容器组件的代码文件当中,这样就无需多个文件。
要实现容器组件和 UI 组件的连接,需要通过 connect 来实现。
// 引入UI组件
import CountUI from '../../components/Count'
// 引入 connect 连接UI组件
import {connect} from 'react-redux'
// 建立连接
export default connect()(CountUI) // 此处没写完,后面还会继续写连接 redux
以后不在导入 UI 组件,而是容器组件,且容器组件需要的 store 是通过上层父组件 props 传递过来的。
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import Count from './containers/Count'
import store from './redux/store'
export default class APP extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<Count store={store} />
</div>
)
}
}2)容器与 UI 组件操作
查看 react-redux 模型图时,会发现容器组件需要给 UI 组件传递状态和方法,并且是通过 props 来传递,看起来很简单。但是,我们会发现容器组件中似乎没有我们平常传递 props 的情形。
这时候就需要继续研究一下容器组件中的唯一一个函数 connect。
connect 方法是一个连接器,用于连接容器组件和 UI 组件。它第一次执行时,接收 4 个参数,这些参数都是可选的,它执行的执行结果还是一个函数,第二次执行接收一个 UI 组件(需引入)。
// [] 表示可选。我们只学习前两个参数
connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps, [mergeProps], [options])(UI 组件)mapStateToProps
const mapStateToProps = state => ({ count: state })接收 state 作为参数。这个 state 是插件调完了 state.getState() 后的值,然后插件调用 mapStateToProps 时,会把 state.getState() 后的值作为实参传递到 mapStateToProps 函数。
mapStateToProps 返回值是一个对象。其中,对象的 key 会作为 UI 组件 props 的 key,而值会作为 value --- state。
如上面的代码,在 UI 组件中直接通过 props 来读取 count 值。
<h1>当前求和为:{this.props.count}</h1>这样我们就打通了 UI 组件和容器组件间的状态传递,那如何传递方法呢?
mapDispatchToProps
connect 接受的第二个参数是 mapDispatchToProps 它是用于建立 UI 组件的参数到 store.dispacth 方法的映射。
// 完整版 - 1
// 语法层面优化
function mapDispatchToProps(dispatch){
return {
jia:number => dispatch(createIncrementAction(number)),
jian:number => dispatch(createDecrementAction(number)),
jiaAsync:(number,timer) => dispatch(createIncrementAsyncAction(number,timer)),
}
}
connect(..., mapDispatchToProps, ...)(UI 组件)
// *****************************************************************************************
// 完整版 - 2
// 语法层面优化
connect(..., dispatch => ({
jia:number => dispatch(createIncrementAction(number)),
jian:number => dispatch(createDecrementAction(number)),
jiaAsync:(number,timer) => dispatch(createIncrementAsyncAction(number,timer)),
}), ...)(UI 组件)其实 mapDispatchToProps 方法不仅可以传递函数,也可以传递对象。在这里面定义 action 执行的方法,例如 jia 执行什么函数,jian 执行什么函数?
// 简写
connect(..., {
jia: createIncrementAction,
jian: createDecrementAction,
jiaAsync: createIncrementAsyncAction
}, ...)(UI 组件)似乎少了点什么,在这里调用了函数,创建了 action 对象,但是好像 store 并没有执行 dispatch,那是不是断了呢?执行不了呢?
其实这里 react-redux 已经帮我们做了优化,当调用 actionCreator 的时候,会立即发送 action 给 store,而不用手动的 dispatch,也就是自动调用 dispatch。
this.props.jia(5)
// 这等同于
dispatch(createIncrementAction(5))3)优化
[1] 不用在写 subscribe 方法
自动就会监听 state 的改变,然后重新解析模板。因为都藏在了 connect 这个函数里了。
// 不用在写了。
/*
connect 函数创建了一个包装组件,这个包装组件会:
a. 订阅 Redux store 的变化
b. 当相关的 state 改变时,自动重新渲染被包装的组件
*/
store.subscribe(() => {
ReactDOM.render( <App /> , document.getElementById('root'))
})[2] Provider
由于我们的状态可能会被很多组件使用,所以 React-Redux 给我们提供了一个 Provider 组件,可以全局注入 redux 中的 store ,只需要把 Provider 注册在根部组件即可。
例如,当以下组件都需要使用 store 时,我们需要这么做,但是这样徒增了工作量,很不便利。
<Count store={store}/>
{/* 示例 */}
<Demo1 store={store}/>
<Demo1 store={store}/>
<Demo1 store={store}/>
<Demo1 store={store}/>
<Demo1 store={store}/>我们可以这么做:在 src 目录下的 index.js 文件中,引入 Provider,直接用 Provider 标签包裹 App 组件,将 store 写在 Provider 中即可。
import {Provider} from 'react-redux'
import store from './redux/store'
ReactDOM.render(
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>,
document.getElementById("root")
);这样我们在 App.jsx 文件中,组件无需手写指定 store,即可使用 store。
[3] 整合UI组件与容器组件
删除 components 文件夹,把 UI 组件移动到 containers 文件夹里。大致整合思路如下:
import { Component } from 'react'
import { connect } from 'react-redux'
import { actionCreator1, actionCreator2 } from '../redux/actions'
// UI 组件
class Xxx extends Component {
render() {
return (
// JSX
)
}
}
// mapStateToProps 函数
const mapStateToProps = (state) => ({
// 将需要的 state 映射到 props
})
// mapDispatchToProps 对象
const mapDispatchToProps = {
action1: actionCreator1,
action2: actionCreator2
}
// 容器组件
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(Xxx)二、函数式组件操作
store 与 reducer、action 与前面创建方式一样,只不过不在使用 connect 连接了。在函数式组件中通过两个钩子函数来操作 state。
访问数据
const state = useSelector(state => state);react-redux 为我们提供一个钩子函数 useSelector,用于获取 Redux 中存储的数据,它需要一个回调函数作为参数,回调函数的第一个参数就是当前的 state,回调函数的返回值,会作为 useSelector 的返回值返回。
操作数据
const dispatch = useDispatch();useDispatch 同样是 react-redux 提供的钩子函数,用来获取 redux 的派发器,对 state 的所有操作都需要通过派发器来进行。
第三章:Redux Toolkit
一、走进 Redux Toolkit
1. 是什么?
Redux Toolkit 是 Redux 官方推荐的编写 Redux 逻辑的方法。 它包含我们对于构建 Redux 应用程序必不可少的包和函数。 Redux Toolkit 的构建简化了大多数 Redux 任务,防止了常见错误,并使编写 Redux 应用程序变得更加容易。可以说 Redux Toolkit 就是目前 Redux 的最佳实践方式。
为了方便后面内容,之后 Redux Toolkit 简称 RTK。
总结:它提供了一系列的工具方法来简化 Redux 应用的开发和维护。
2. 目的
Redux 核心库是故意设计成非定制化的样子(unopinionated)。怎么做完全取决于你,例如配置 store,你的 state 存什么东西,以及如何构建 reducer。
有些时候这样挺好,因为有很高的灵活性,但我们又不总是需要这么高的自由度。有时,我们只是想以最简单的方式上手,并想要一些良好的默认行为能够开箱即用。或者,也许你正在编写一个更大的应用程序并发现自己正在编写一些类似的代码,而你想减少必须手工编写的代码量。
Redux Toolkit 它最初是为了帮助解决有关 Redux 的三个常见问题而创建的:
- "配置 Redux store 过于复杂"
- "我必须添加很多软件包才能开始使用 Redux"
- "Redux 有太多样板代码"
3. 为什么需要使用 Redux Toolkit
通过遵循我们推荐的最佳实践,提供良好的默认行为,捕获错误并让你编写更简单的代码,React Toolkit 使得编写好的 Redux 应用程序以及加快开发速度变得更加容易。Redux Toolkit 对所有 Redux 用户都有帮助,无论技能水平或者经验如何。可以在新项目开始时添加它,也可以在现有项目中将其用作增量迁移的一部分。
二、快速入门
1. 安装 RTK
无论是 RTK 还是 Redux,在 React 中使用时,react-redux 都是必不可少。所以使用 RTK 依然需要安装两个包:react-redux 和 @reduxjs/toolkit。
npm install react-redux @reduxjs/toolkit -S
# 或者
yarn add react-redux @reduxjs/toolkit2. 基础开发流程
安装完相关包以后,就可以开始编写基本的 RTK 程序了。
- 创建一个 store 文件夹。
- 创建一个 index.js 做为主入口。
- 创建一个 features (也可以起名为 modules) 文件夹用来装所有的 store。
- 在 festures 文件夹下创建一个 counterSlice.js 文件,并导出简单的加减方法。
[1] 创建 Redux State Slice
创建 slice 需要一个字符串名称来标识切片、一个初始 state 以及一个或多个定义了该如何更新 state 的 reducer 函数。slice 创建后 ,我们可以导出 slice 中生成的 Redux action creators 和 reducer 函数。
@/store/features/counterSlice.js
import { createSlice } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
const initialState = {
value: 0,
}
// 创建一个Slice
export const counterSlice = createSlice({
name: 'counter',
initialState,
reducers: {
// 定义一个加的方法
increment: state => {
state.value += 1
},
// 定义一个减的方法
decrement: state => {
state.value -= 1
},
}
})
console.log('counterSlice', counterSlice)
console.log('counterSlice.actions', counterSlice.actions)
// 导出加减方法
export const { increment, decrement } = counterSlice.actions
// 暴露reducer
export default counterSlice.reducercreateSlice 是一个全自动的创建 reducer 切片的方法,在它的内部调用就是 createAction 和 createReducer,之所以先介绍那两个也是这个原因。createSlice 需要一个对象作为参数,对象中通过不同的属性来指定 reducer 的配置信息。
createSlice(configuration object)配置对象中的属性:
- name —— reducer 的名字,会作为 action 中 type 属性的前缀,不要重复。
- initialState —— state 的初始值。
- reducers —— reducer 的具体方法,需要一个对象作为参数,可以以方法的形式添加 reducer,RTK 会自动生成 action 对象。
总的来说,使用 createSlice 创建切片后,切片会自动根据配置对象生成 action 和 reducer,action 需要导出给调用处,调用处可以使用 action 作为 dispatch 的参数触发 state 的修改。reducer 需要传递给 configureStore 以使其在仓库中生效。
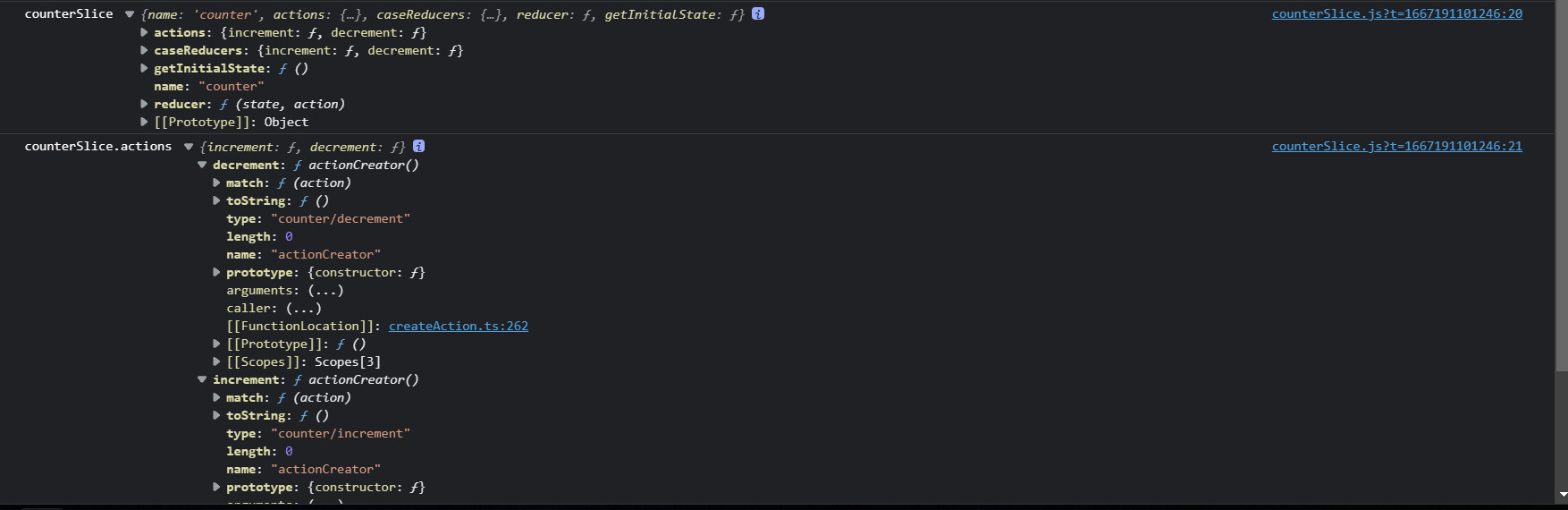
我们可以看看 counterSlice 和 counterSlice.actions 是什么样子?
[2] 将 Slice Reducers 添加到 Store 中
下一步,我们需要从计数切片中引入 reducer 函数,并将它添加到我们的 store 中。通过在 reducer 参数中定义一个字段,我们告诉 store 使用这个 slice reducer 函数来处理对该状态的所有更新。
我们以前直接用 redux 是这样的。
const reducer = combineReducers({
counter:counterReducers
});
const store = createStore(reducer);@/store/index.js
切片的 reducer 属性是切片根据我们传递的方法自动创建生成的 reducer,需要将其作为 reducer 传递进 configureStore 的配置对象中以使其生效:
import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
import counterSlice from './features/counterSlice'
// configureStore创建一个redux数据
const store = configureStore({
// 合并多个Slice
reducer: {
counter: counterSlice,
},
devTools: true,
})
export default store- configureStore 需要一个对象作为参数,在这个对象中可以通过不同的属性来对 store 进行设置,比如:reducer 属性用来设置 store 中关联到的 reducer,preloadedState 用来指定 state 的初始值等,还有一些值我们会放到后边讲解。
- reducer 属性可以直接传递一个 reducer,也可以传递一个对象作为值。如果只传递一个 reducer,则意味着 store 中只有一个 reducer。若传递一个对象作为参数,对象的每个属性都可以执行一个 reducer,在方法内部它会自动对这些 reducer 进行合并。
[3] store 加到全局
src/index.js
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client'
import App from './App'
// redux toolkit
import { Provider } from 'react-redux'
import store from './store'
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root')).render(
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>,
)[4] 在 React 组件中使用 Redux 状态和操作
现在我们可以使用 React-Redux 钩子让 React 组件与 Redux store 交互。我们可以使用 useSelector 从 store 中读取数据,使用 useDispatch(dispatch 传入 actions)。
@/App.jsx
import React from 'react'
import { useDispatch, useSelector } from 'react-redux'
// 引入对应的方法
import { increment, decrement } from './store/features/counterSlice'
export default function App() {
const count = useSelector(state => state.counter.value)
const dispatch = useDispatch()
return (
<div style={{ width: 100, margin: '100px auto' }}>
<button onClick={() => dispatch(increment())}>+</button>
<span>{count}</span>
<button onClick={() => dispatch(decrement())}>-</button>
</div>
)
}这里如果使用类式组件,依旧使用的是 connent 函数。
小总结
这是关于如何通过 React 设置和使用 Redux Toolkit 的简要概述。 回顾细节:
- 使用 configureStore 创建 Redux store
- configureStore 接受 reducer 函数作为命名参数
- configureStore 会使用默认设置自动配置 store
- 为 React 应用程序组件提供 Redux store
- 使用 React-Redux
<Provider>组件包裹你的<App />- 传递 Redux store 如
<Provider store={store}>- 使用 createSlice 创建 Redux "slice" reducer
- 使用字符串名称、初始状态和命名的 reducer 函数调用“createSlice”
- Reducer 函数可以使用 Immer 来“改变”状态
- 导出生成的 slice reducer 和 action creators
- 在 React 组件中使用 React-Redux useSelector/useDispatch 钩子
- 使用 useSelector 钩子从 store 中读取数据
- 使用 useDispatch 钩子获取 dispatch 函数,并根据需要 dispatch actions
三、其他使用
1. Action Payloads
1)传递基本类型参数
上面的例子实现了固定的加一减一,但如果想加多少就能动态加多少,怎么办?
就需要传参。那如何传参呢?
第一步:定义接受参数
接收参数的方式和 redux 一样,可以通过 action 来接收参数,如下:
store/features/counterSlice.js
import { createSlice } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
// 创建一个Slice
export const counterSlice = createSlice({
// ...
reducers: {
incrementByAmount: (state, action) => {
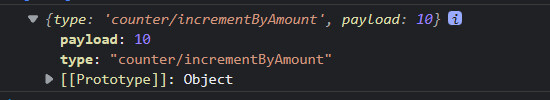
// action 里面有 type 和 payload 两个属性,所有的传参都在payload里面
console.log(action)
state.value += action.payload
},
},
})
// 导出加减方法
export const { increment, decrement, incrementByAmount } = counterSlice.actions
// 暴露reducer
export default counterSlice.reducerincrementByAmount 的 action 参数。
第二步:传递参数
和 redux 的传参一样,如下:
import React, { useState } from 'react'
import { useDispatch, useSelector } from 'react-redux'
// 引入对应的方法
import { incrementByAmount } from './store/features/counterSlice'
export default function App() {
const count = useSelector(state => state.counter.value)
const dispatch = useDispatch()
const [amount, setAmount] = useState(1)
return (
<div style={{ width: 500, margin: '100px auto' }}>
<input type="text" value={amount} onChange={e => setAmount(e.target.value)} />
<button onClick={() => dispatch(incrementByAmount(Number(amount) || 0))}> Add Amount </button>
<span>{count}</span>
</div>
)
}注意:这里 reducer 的 action 中如果要传入参数,只能是一个 payload,如果是多个参数的情况,那就需要封装成一个 payload 的对象。
2)传递对象参数
以一个常见的 todo 案例来讲解。
在 store/features/todoSlice.js 文件中,可能你会写这样的伪代码。
import { createSlice, nanoid } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
const initialState = {
todoList: [],
}
// 创建一个 Slice
export const todoSlice = createSlice({
name: 'todo',
initialState,
reducers: {
addTodo: (state, action) => {}
},
},
})
// 导出加减方法
export const { addTodo } = todoSlice.actions
// 暴露reducer
export default todoSlice.reducerstore/index.js
import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
import counterSlice from './features/counterSlice'
import todoSlice from './features/todoSlice'
// configureStore 创建一个 redux 数据
const store = configureStore({
// 合并多个 Slice
reducer: {
counter: counterSlice,
todo: todoSlice,
},
})
export default storeTodo.jsx
import React from 'react'
import { useDispatch, useSelector } from 'react-redux'
// 引入对应的方法
import { addTodo } from '../store/features/todoSlice'
export default function Todo() {
const todoList = useSelector(state => state.todo.todoList)
const dispatch = useDispatch()
return (
<div>
<p>任务列表</p>
<ul>
{todoList.map(todo => (
<li key={todo.id}>
<input type="checkbox" defaultChecked={todo.completed} /> {todo.content}
</li>
))}
</ul>
<button onClick={() => dispatch(addTodo('敲代码'))}>增加一个todo</button>
</div>
)
}我们刚刚看到 createSlice 中的 action creator 通常期望一个参数,它变成了 action.payload。这简化了最常见的使用模式,但有时我们需要做更多的工作来准备 action 对象的内容。 在我们的 postAdded 操作的情况下,我们需要为新 todo 生成一个唯一的 ID,我们还需要确保有效 payload 是一个看起来像 {id, content, completed} 的对象。
现在,我们正在 React 组件中生成 ID 并创建有效 payload 对象,并将有效 payload 对象传递给 addTodo。 但是,如果我们需要从不同的组件 dispatch 相同的 action,或者准备 payload 的逻辑很复杂怎么办? 每次我们想要 dispatch action 时,我们都必须复制该逻辑,并且我们强制组件确切地知道此 action 的有效 payload 应该是什么样子。
注意:如果 action 需要包含唯一 ID 或其他一些随机值,请始终先生成该随机值并将其放入 action 对象中。Reducer 中永远不应该计算随机值,因为这会使结果不可预测。
幸运的是,createSlice 允许我们在编写 reducer 时定义一个 prepare 函数。prepare 函数可以接受多个参数,生成诸如唯一 ID 之类的随机值,并运行需要的任何其他同步逻辑来决定哪些值进入 action 对象。然后它应该返回一个包含 payload 字段的对象。(返回对象还可能包含一个 meta 字段,可用于向 action 添加额外的描述性值,以及一个 error 字段,该字段应该是一个布尔值,指示此 action 是否表示某种错误。)
rtk 还提供了一个 nanoid 方法,用于生成一个固定长度的随机字符串,类似 uuid 功能。
import { createSlice, nanoid } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
// 创建一个 Slice
export const todoSlice = createSlice({
name: 'todo',
initialState,
reducers: {
addTodo: {
// 这个函数就是我们平时直接写在这的函数( addTodo: (state, action) => {} )
reducer(state, aciton) {
console.log('addTodo-reducer执行')
const { id, content } = aciton.payload
state.todoList.push({ id, content, completed: false })
},
// 预处理函数,返回值就是 reducer 函数接收的 pyload 值, 必须返回一个带有 payload 字段的对象
prepare(content) {
console.log('prepare参数', content)
return {
payload: {
id: nanoid(),
content,
},
}
},
},
},
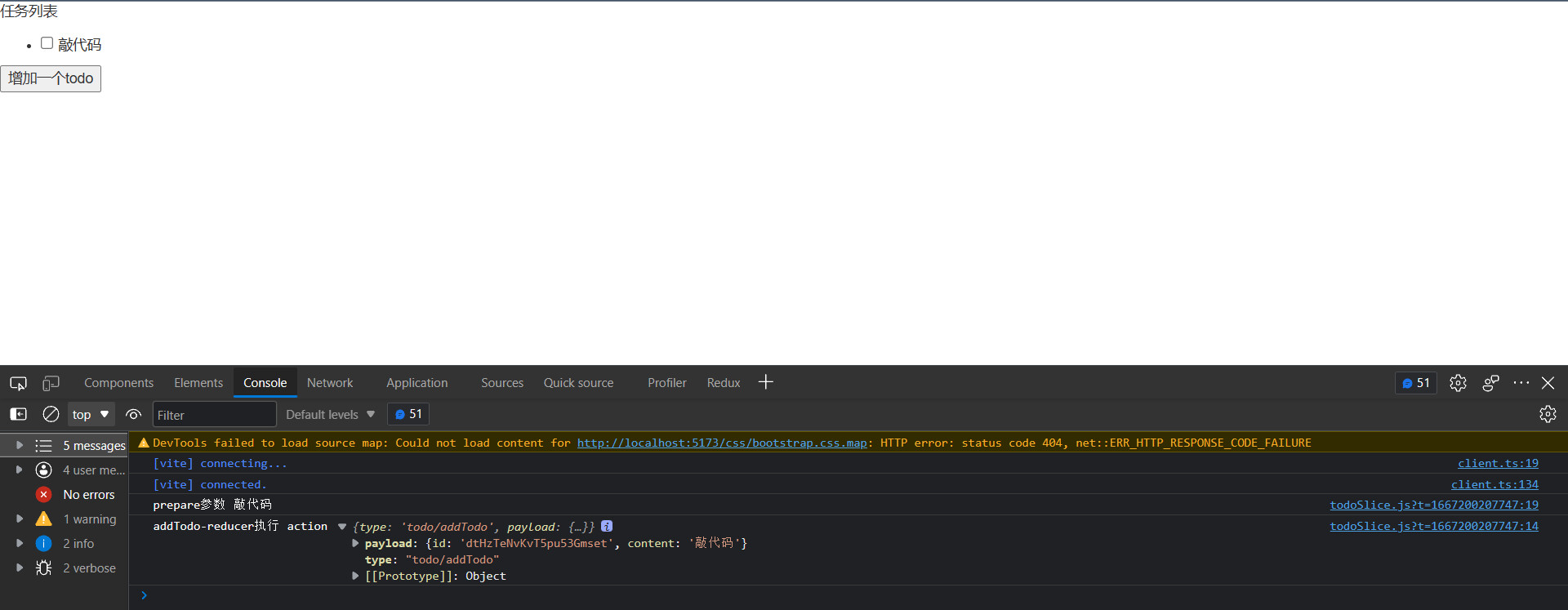
})可以打印 dispatch(addTodo(’敲代码‘)) 的结果看到,返回了一个带有 payload 字段的 action。
2. 异步逻辑与数据请求
1)异步逻辑
[1] Thunks 与异步逻辑
就其本身而言,Redux store 对异步逻辑一无所知。它只知道如何同步 dispatch action,通过调用 root reducer 函数更新状态,并通知 UI 某些事情发生了变化。任何异步都必须发生在 store 之外。
但是,如果希望通过调度或检查当前 store 状态来使异步逻辑与 store 交互,该怎么办? 这就是 Redux middleware 的用武之地。
[2] Thunk 函数
thunk 最重要的思想,就是可以接受一个返回函数的 action creator。如果这个 action creator 返回的是一个函数,就执行它,如果不是,就按照原来的 action 执行。
正因为这个 action creator 可以返回一个函数,那么就可以在这个函数中执行一些异步的操作。
Thunks 通常还可以使用 action creator 再次 dispatch 普通的 action,比如 dispatch(increment())。
为了与 dispatch 普通 action 对象保持一致,我们通常将它们写为 thunk action creators,它返回 thunk 函数。
const incrementAsync = amount => {
return (dispatch, getState) => {
setTimeout(() => {
dispatch(incrementByAmount(amount))
}, 1000)
}
}incrementAsync 函数就返回了一个函数,将 dispatch 作为函数的第一个参数传递进去,在函数内进行异步操作就可以了。
Thunk 通常写在 “slice” 文件中。createSlice 本身对定义 thunk 没有任何特殊支持,因此你应该将它们作为单独的函数编写在同一个 slice 文件中。这样,他们就可以访问该 slice 的普通 action creator,并且很容易找到 thunk 的位置。
[3] 案例
改写之前的计数器,增加一个延时器。
@/store/features/counterSlice.js
import { createSlice } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
const initialState = {
value: 0
}
// 创建一个 Slice
export const counterSlice = createSlice({
name: 'counter',
initialState,
reducers: {
incrementByAmount: (state, action) => {
// action 里面有 type 和 payload 两个属性,所有的传参都在 payload 里面
state.value += action.payload
},
}
})
const { incrementByAmount } = counterSlice.actions
export const incrementAsync = amount => {
return (dispatch, getState) => {
const stateBefore = getState()
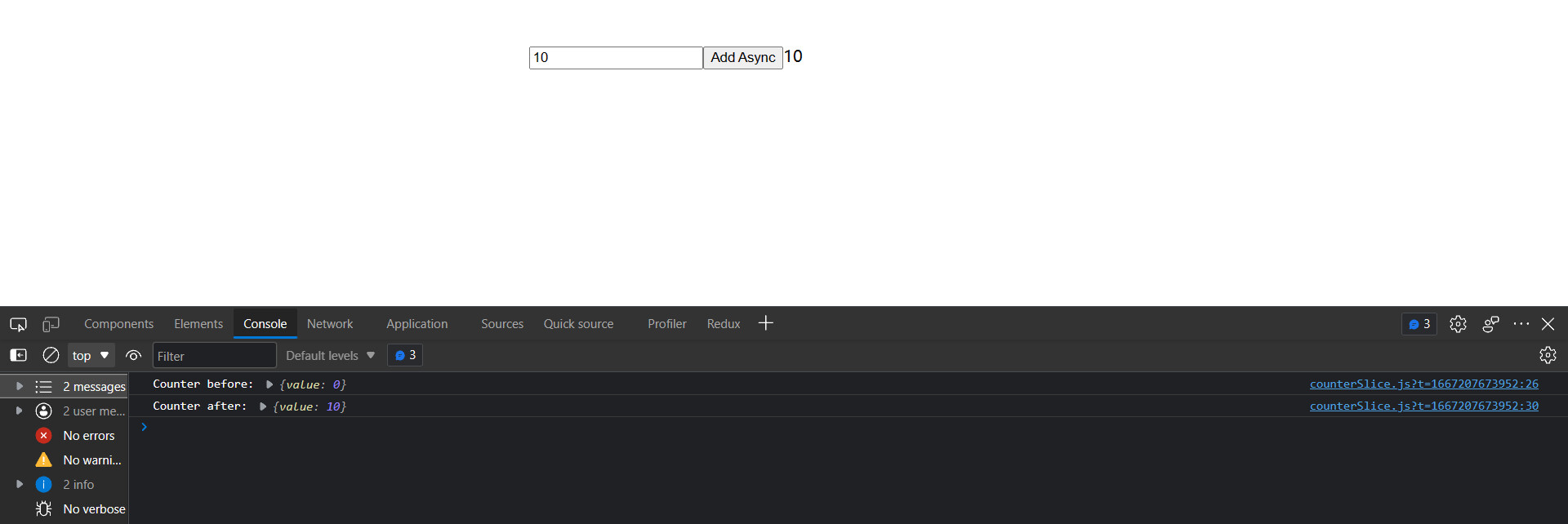
console.log('Counter before:', stateBefore.counter)
@/App.jsx
import React, { useState } from 'react'
import { useDispatch, useSelector } from 'react-redux'
// 引入对应的方法
import { incrementAsync } from './store/features/counterSlice'
export default function App() {
const count = useSelector(state => state.counter.value)
const dispatch = useDispatch()
const [amount, setAmount] = useState(1)
return (
<div style={{ width: 500, margin: '100px auto' }}>
<input type="text" value={amount} onChange={e => setAmount(e.target.value)} />
<button onClick={() => dispatch(incrementAsync(Number(amount) || 0))}> Add Async </button>
<span>{count}</span>
</div>
)
}
2)编写异步 Thunks
[1] 引言
Thunk 内部可能有异步逻辑,例如 setTimeout、Promise 和 async/await。这使它们成为使用 AJAX 发起 API 请求的好地方。
Redux 的数据请求逻辑通常遵循以下可预测的模式:
- 在请求之前 dispatch 请求“开始”的 action,以指示请求正在进行中。这可用于跟踪加载状态以允许跳过重复请求或在 UI 中显示加载中提示。
- 发出异步请求。
- 根据请求结果,异步逻辑 dispatch 包含结果数据的“成功” action 或包含错误详细信息的“失败” action。在这两种情况下,reducer 逻辑都会清除加载状态,并且要么展示成功案例的结果数据,要么保存错误值并在需要的地方展示。
这些步骤不是必需的,而是常用的。(如果你只关心一个成功的结果,你可以在请求完成时发送一个“成功” action,并跳过“开始”和“失败” action)
Redux Toolkit 提供了一个 createAsyncThunk API 来实现这些 action 的创建和 dispatch。
手动编写一个典型的 async thunk 的代码,它可能看起来像这样:
const getRepoDetailsStarted = () => ({
type: 'repoDetails/fetchStarted'
})
const getRepoDetailsSuccess = repoDetails => ({
type: 'repoDetails/fetchSucceeded',
payload: repoDetails
})
const getRepoDetailsFailed = error => ({
type: 'repoDetails/fetchFailed',
error
})
const fetchIssuesCount = (org, repo) => async dispatch => {
dispatch(getRepoDetailsStarted())
try {
const repoDetails = await getRepoDetails(org, repo)
dispatch(getRepoDetailsSuccess(repoDetails))
} catch (err) {
dispatch(getRepoDetailsFailed(err.toString()))
}
}但是,使用这种方法编写代码很乏味。每个单独的请求类型都需要重复类似的实现:
- 需要为三种不同的情况定义独特的 action 类型。
- 每种 action 类型通常都有相应的 action creator 功能。
- 必须编写一个 thunk 以正确的顺序发送正确的 action。
createAsyncThunk 实现了这套模式:通过生成 action type 和 action creator 并生成一个自动 dispatch。这些 action 的 thunk,你提供一个回调函数来进行异步调用,并把结果数据返回成 Promise。
[2] 使用 createAsyncThunk 请求数据
Redux Toolkit 的 createAsyncThunk API 生成 thunk,会自动 dispatch 那些"start/success/failure" action。
从添加一个 thunk 开始,该 thunk 将进行 AJAX 调用。
@/store/features/counterSlice.js
import { createSlice, createAsyncThunk } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
// 请求电影列表
const reqMovieListApi = () =>
fetch(
'https://pcw-api.iqiyi.com/search/recommend/list?channel_id=1&data_type=1&mode=24&page_id=1&ret_num=48',
).then(res => res.json())
const initialState = {
status: 'idel',
list: [],
totals: 0,
}
// thunk 函数允许执行异步逻辑, 通常用于发出异步请求。
// createAsyncThunk 创建一个异步 action,方法触发的时候会有三种状态:
// pending(进行中)、fulfilled(成功)、rejected(失败)
export const getMovieData = createAsyncThunk('movie/getMovie', async () => {
const res = await reqMovieListApi()
return res.data
})createAsyncThunk 接收 2 个参数:
- 第一个参数:将用作生成的 action 类型的前缀的字符串。
- 第二个参数: “payload creator”回调函数,它应该返回一个包含一些数据的 Promise,或者一个被拒绝的带有错误的 Promise。
Payload creator 通常会进行某种 AJAX 调用,并且可以直接从 AJAX 调用返回 Promise,或者从 API 响应中提取一些数据并返回。我们通常使用 JS async/await 语法来编写它,这让我们可以编写使用 Promise 的函数,同时使用标准的 try/catch 逻辑而不是 somePromise.then() 链式调用。
在这种情况下,我们传入 'movie/getMovie' 作为 action 类型的前缀。我们的 payload 创建回调等待 API 调用返回响应。响应对象的格式为 {data: []},我们希望我们 dispatch 的 Redux action 有一个 payload,也就是电影列表的数组。所以,我们提取 response.data,并从回调中返回它。
当调用 dispatch(getMovieData()) 的时候,getMovieData 这个 thunk 会首先 dispatch 一个 action 类型为 'movie/getMovie/pending':
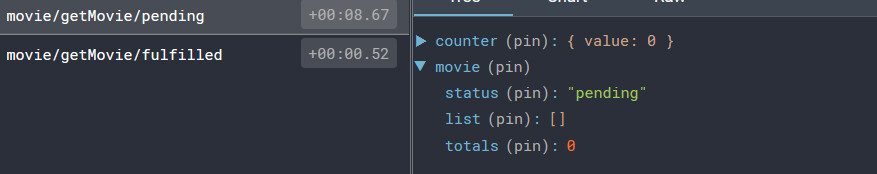
我们可以在我们的 reducer 中监听这个 action 并将请求状态标记为 “loading 正在加载”。
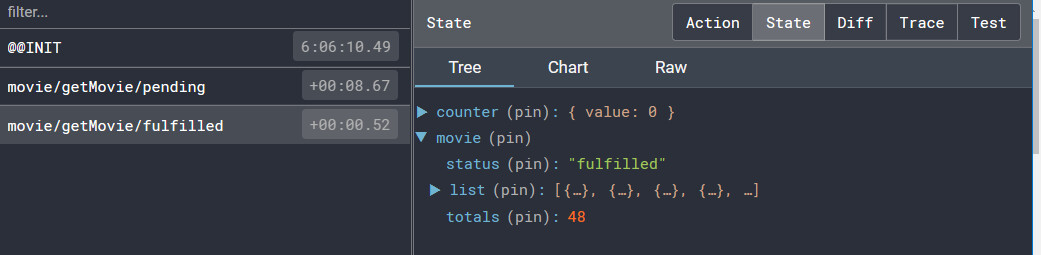
一旦 Promise 成功,getMovieData thunk 会接受我们从回调中返回的 response.data,并 dispatch 一个 action,action 的 payload 为接口返回的数据(response.data),action 的 类型为 'movie/getMovie/fulfilled'。
[3] 使用 extraReducers
有时 slice 的 reducer 需要响应没有定义到该 slice 的 reducers 字段中的 action。这个时候就需要使用 slice 中的 extraReducers 字段。
extraReducers 选项是一个接收名为 builder 的参数的函数。builder 对象提供了一些方法,让我们可以定义额外的 case reducer,这些 reducer 将响应在 slice 之外定义的 action。我们将使用 builder.addCase(actionCreator, reducer) 来处理异步 thunk dispatch 的每个 action。
在这个例子中,我们需要监听我们 getMovieData thunk dispatch 的 "pending" 和 "fulfilled" action 类型。这些 action creator 附加到我们实际的 getMovieData 函数中,我们可以将它们传递给 extraReducers 来监听这些 action:
const initialState = {
status: 'idel',
list: [],
totals: 0,
}
export const getMovieData = createAsyncThunk('movie/getMovie', async () => {
const res = await reqMovieListApi()
return res.data
})
// 创建一个 Slice
export const movieSlice = createSlice({
name: 'movie',
initialState,
// extraReducers 字段让 slice 处理在别处定义的 actions,
// 包括由 createAsyncThunk 或其他 slice 生成的 actions。
extraReducers(builder) {
builder
.addCase(getMovieData.pending, state => {
console.log('🚀 ~ 进行中!')
state.status = 'pending'
})
.addCase(getMovieData.fulfilled, (state, action) => {
console.log('🚀 ~ fulfilled', action.payload)
state.status = 'pending'
state.list = state.list.concat(action.payload.list)
state.totals = action.payload.list.length
})
.addCase(getMovieData.rejected, (state, action) => {
console.log('🚀 ~ rejected', action)
state.status = 'pending'
state.error = action.error.message
})
},
})
// 默认导出
export default movieSlice.reducer我们将根据返回的 Promise 处理可以由 thunk dispatch 的三种 action 类型:
- 当请求开始时,我们将 status 枚举设置为 'pending'。
- 如果请求成功,我们将 status 标记为 'pending',并将获取的电影列表添加到 state.list。
- 如果请求失败,我们会将 status 标记为 'pending',并将任何错误消息保存到状态中以便我们可以显示它。
createAsyncThunk 可以写在任何一个 slice 的 extraReducers 中,它接收 2 个参数。
生成 action的 type 值。这里 type 是要自己定义,不像是 createSlice 自动生成 type。这就要注意避免命名冲突问题了,如果 createSlice 定义了相同的 name 和方法,就会冲突的。
包含数据处理的 promise。首先会 dispatch 一个 action 类型为 movie/getMovie/pending,当异步请求完成后,根据结果成功或是失败,决定 dispatch 出 action 的类型为 movie/getMovie/fulfilled 或 movie/getMovie/rejected,这三个 action 可以在 slice 的 extraReducers 中进行处理。
这个 promise 也只接收 2 个参数,分别是 payload 和包含了 dispatch、getState 的 thunkAPI 对象,所以除了在 slice 的 extraReducers 中处理之外,createAsyncThunk 中也可以调用任意的 action,这样就很像原本 thunk 的写法了,并不推荐。==> 参见第三种写法。
除了上面的写法,还可以:
extraReducers: {
[fetchHomeMultidataAction.pending](state, action) {
console.log("fetchHomeMultidataAction pending")
},
[fetchHomeMultidataAction.fulfilled](state, { payload }) {
state.banners = payload.data.banner.list
state.recommends = payload.data.recommend.list
},
[fetchHomeMultidataAction.rejected](state, action) {
console.log("fetchHomeMultidataAction rejected")
}
}第三种写法:
在派发事件时候 dispatch(fetchHomeMultidataAction(数据)),extraInfo 就会接受到数据。除此之外,还会给我们传递 store 对象。我们就可以在这里直接把数据存到 redux 中,而不用写 extraReducers。
export const fetchHomeMultidataAction = createAsyncThunk(
"fetch/homemultidata",
async (extraInfo, { dispatch, getState }) => {
// console.log(extraInfo, dispatch, getState)
// 1.发送网络请求, 获取数据
const res = await axios.get("http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata")
// 2.取出数据, 并且在此处直接dispatch操作(可以不做)
const banners = res.data.data.banner.list
const recommends = res.data.data.recommend.list
dispatch(changeBanners(banners))
dispatch(changeRecommends(recommends))
// 3.返回结果, 那么action状态会变成fulfilled状态
return res.data
})第四章:原理
一、combineReducers 原理
combineReducers 是 Redux 库的一个函数,它的主要作用是将多个 reducer 函数合并成一个。
combineReducers 函数接收一个对象,这个对象的键是 state 的字段名,值是管理这个字段的 reducer。然后 combineReducers 返回一个新的 reducer 函数。这个新的 reducer 函数会遍历 combineReducers 接收到的对象,调用每个 reducer,并将返回的结果组合成一个新的 state 对象。
import { combineReducers } from 'redux';
const userReducer = (state = {}, action) => {
// ...
};
const postsReducer = (state = [], action) => {
// ...
};
const reducer = combineReducers({
user: userReducer,
posts: postsReducer
});
// combineReducers 返回一个函数,这个函数做的事情如下
function reducer(state = {}, action) {
// 返回一个对象, store 的 state
return {
user: userReducer(state.user, action),
posts: postsReducer(state.posts, action)
}
}reducer 是一个新的 reducer,它会调用 userReducer 和 postsReducer,并将返回的结果组合成一个新的 state 对象,这个对象的 user 字段由 userReducer 管理,posts 字段由 postsReducer 管理。
当 reducer 接收到一个 action 时,它会将这个 action 和当前的 state 传递给 userReducer 和 postsReducer。然后,它会将 userReducer 和 postsReducer 返回的结果组合成一个新的 state 对象。
二、Redux Toolkit 的数据不可变性
在使用 redux 的 reducer 中常常需要浅拷贝。而使用 Redux Toolkit 时,可以直接修改。为什么?
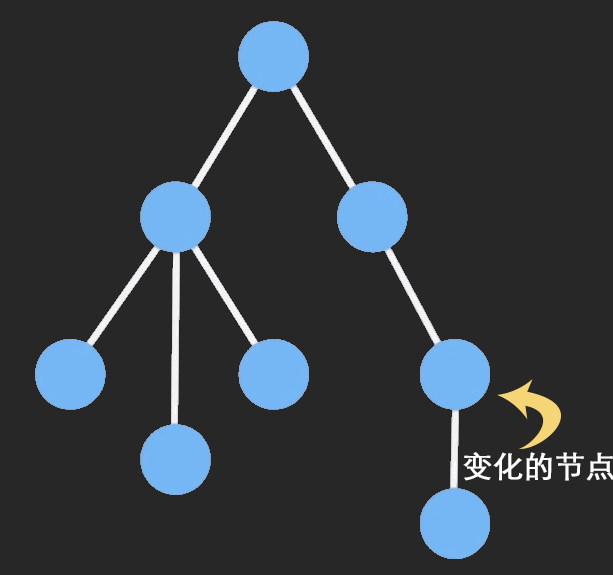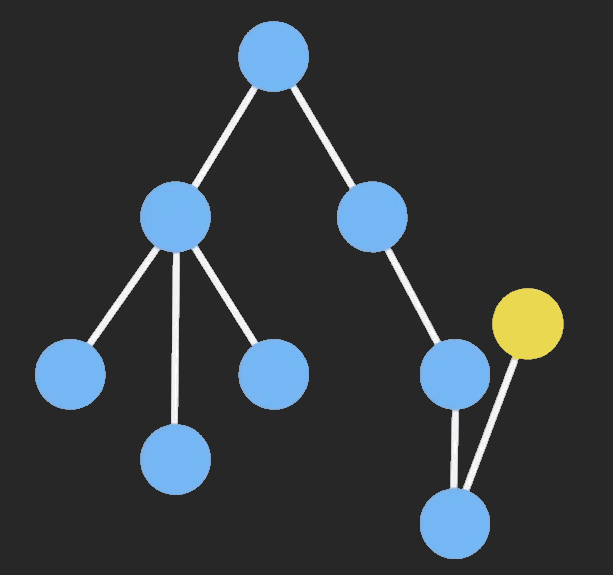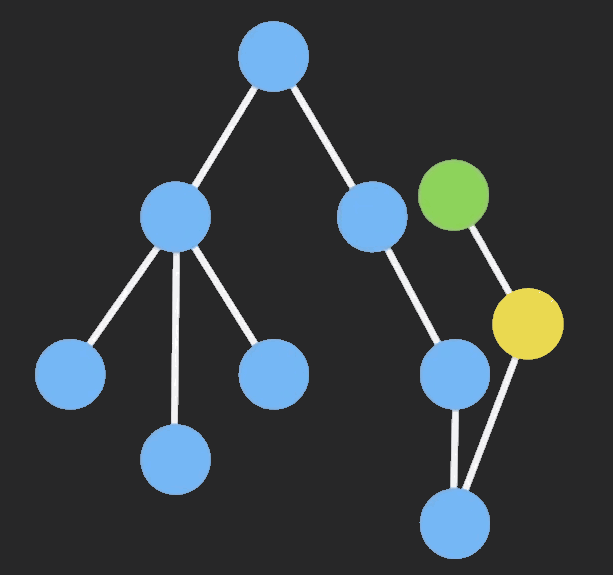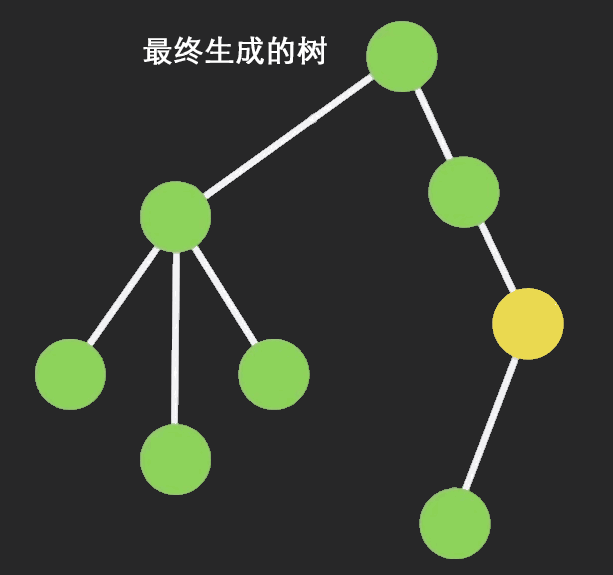
Redux Toolkit 底层使用了 immerjs 库来保证数据的不可变性。
为了节约内存,又出现了一个新的算法:Persistent Data Structure(持久化数据结构或一致性数据结构)。当数据被修改时,会返回一个对象,但是新的对象会尽可能的利用之前的数据结构而不会对内存造成浪费。
三、Redux connect 函数的实现原理
1. 基本实现
// connect 的参数:
// 参数一: 函数
// 参数二: 函数
// 返回值: 函数 => 高阶组件
import { PureComponent } from "react"
import store from "@/store"
export function connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps, store) {
// 高阶组件: 函数
return function(WrapperComponent) {
class NewComponent extends PureComponent {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
// 优化性能,结合 PureComponent。只有 store 中这个组件使用的 stae 发生改变时,才会重新渲染
this.state = mapStateToProps(store.getState())
}
componentDidMount() {
this.unsubscribe = store.subscribe(() => {
// this.forceUpdate()
this.setState(mapStateToProps(store.getState()))
})
}
componentWillUnmount() {
this.unsubscribe()
}
render() {
const stateObj = mapStateToProps(store.getState())
const dispatchObj = mapDispatchToProps(store.dispatch)
return <WrapperComponent {...this.props} {...stateObj} {...dispatchObj}/>
}
}
return NewComponent
}
}2. 加入 Context
StoreContext.js
import { createContext } from "react"
export const StoreContext = createContext()connect.js
// connect的参数:
// 参数一: 函数
// 参数二: 函数
// 返回值: 函数 => 高阶组件
import { PureComponent } from "react"
import { StoreContext } from "./StoreContext"
// import store from "../store"
export function connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps, store) {
// 高阶组件: 函数
return function(WrapperComponent) {
class NewComponent extends PureComponent {
constructor(props, context) {
super(props)
this.state = mapStateToProps(context.getState())
}
componentDidMount() {
this.unsubscribe = this.context.subscribe(() => {
// this.forceUpdate()
this.setState(mapStateToProps(this.context.getState()))
})
}
componentWillUnmount() {
this.unsubscribe()
}
render() {
const stateObj = mapStateToProps(this.context.getState())
const dispatchObj = mapDispatchToProps(this.context.dispatch)
return <WrapperComponent {...this.props} {...stateObj} {...dispatchObj}/>
}
}
NewComponent.contextType = StoreContext
return NewComponent
}
}index.js
export { StoreContext } from "./StoreContext"
export { connect } from "./connect"四、Redux 核心原理
1. 打印日志需求
这种技术称为猴补丁(Monkey Patching)。
// 对每次派发的action进行拦截
function log(store) {
// 保存最初的dispatch
const next = store.dispatch
function dispatchWithLog(action) {
console.log('当前派发的action:', action)
// 真正派发的代码: 使用之前的dispatch进行派发
next(action)
console.log('派发之后的结果', store.getState())
}
// monkey patch: 猴补丁 => 篡改现有的代码, 对整体的执行逻辑进行修改
store.dispatch = dispatchWithLog
}2. thunk 中间件的实现
支持派发函数,两个参数:dispatch 和 getState。
function thunk(store) {
const next = store.dispatch
function dispatchWithFn(action) {
if(typeof action === 'function') {
// 传入最新的dispatch,因为可能在派发函数内部继续派发函数
action(store.dispatch, store.getState)
} else {
next(action)
}
}
store.dispatch = dispatchWithFn
}3. applyMiddleware 简单实现
function applyMiddleware(store, ...fns) {
fns.forEach(fn => fn(store))
}
export default applyMiddleware@/store/index.js 中使用
import { createStore, combineReducers } from "redux"
import { log, thunk, applyMiddleware } from "./middleware"
import counterReducer from './counter'
import homeReducer from './home'
import userReducer from './user'
// 将两个reducer合并到一起
const reducer = combineReducers({
counter: counterReducer,
home: homeReducer,
user: userReducer
})
const store = createStore(reducer)
// 实现applyMiddleware
applyMiddleware(store, log, thunk)
export default store